Oxygen Concentrator vs Cylinder — Which Is Safer?
Understanding the Basics
Before comparing safety, let’s first understand how each device works.Oxygen Concentrator
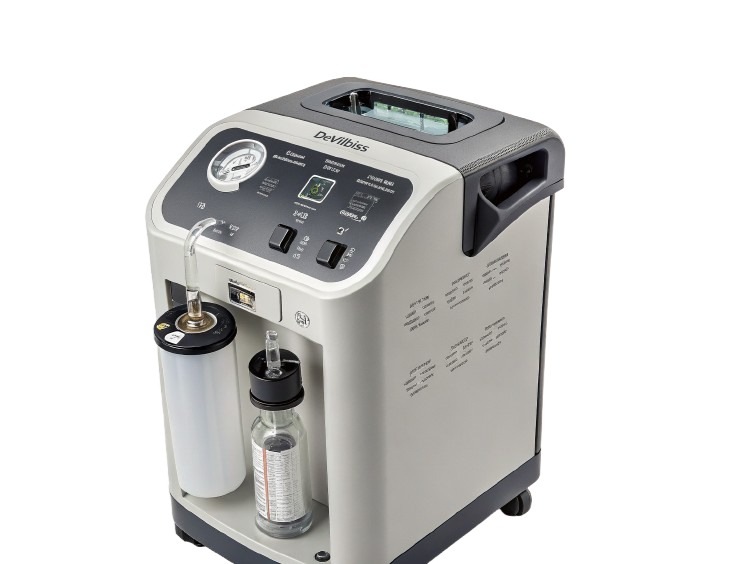
✔An oxygen concentrator is an electrically powered device that draws in ambient air, filters out nitrogen, and delivers concentrated oxygen (usually 90–95% pure) to the patient.✔It provides a continuous flow of oxygen as long as it’s connected to a power source. Concentrators can be portable (battery-operated) or stationary (home use).
Oxygen Cylinder
✔An oxygen cylinder stores compressed medical-grade oxygen gas under high pressure inside a metal tank. The oxygen is released through a regulator and delivered via a nasal cannula or mask. Cylinders come in various sizes, from small portable units to large hospital-grade tanks.✔Both options are medically approved and reliable — but when it comes to safety, the differences are worth understanding.
Safety Comparison: Concentrator vs Cylinder
1. Risk of Explosion or Fire
Oxygen Cylinder: Cylinders store oxygen under high pressure (up to 2000 psi), making them potentially hazardous if mishandled. A damaged or leaking cylinder can lead to fire or explosion risks, especially near flames, electrical sparks, or smoking areas. Improper refilling or rough handling can also be dangerous.✅ Safety Winner: Oxygen Concentrator
2. Power Dependence
Oxygen Cylinder: Cylinders don’t require electricity, making them reliable during power outages or emergencies. They’re often used as backup oxygen sources in hospitals and homes. In areas with frequent power cuts or poor electricity supply, this can be a safety concern if no backup power is available.✅ Safety Winner: Oxygen Cylinder
3. Oxygen Flow and Consistency
Oxygen Cylinder: Oxygen flow is manually controlled using a regulator. Over time, the flow rate can become inconsistent as the pressure decreases, and the cylinder eventually empties. If not monitored, the patient may suddenly run out of oxygen.✅ Safety Winner: Oxygen Concentrator
4. Maintenance and Handling
Oxygen Cylinder: Requires careful handling and periodic refilling by certified suppliers. Each refill increases the risk of contamination if the cylinder isn’t properly cleaned or inspected. Transporting cylinders can also be heavy and cumbersome.✅ Safety Winner: Oxygen Concentrator
When to Choose a Cylinder
An oxygen cylinder is a good choice when:- You live in an area with frequent power cuts.
- You need a backup oxygen source in case your concentrator stops working.
- The oxygen requirement is temporary or occasional.
When to Choose a Concentrator
An oxygen concentrator is ideal if:- You need continuous, long-term oxygen therapy.
- You want a safer, low-maintenance, and cost-effective solution.
- You have access to stable electricity or a reliable backup battery.
Oxygen Concentrator Sale DeVilbiss brand is well-known for its durable, high-quality oxygen concentrators.These machines with features like quiet performance, steady oxygen flow, and easy maintenance, they’re an excellent choice for
Step-by-step guide - How to use an oxygen concentrator safely at home” oxygen concentrator have become essential medical devices for people with respiratory conditions such as COPD, asthma, pneumonia, and
Oxygen Concentrator vs Cylinder – Which Is Better for Home Use? When it comes to home oxygen therapy, choosing the right device is crucial for your health, comfort, and safety.
How Much Does Oxygen Concentrator Rental Cost in Chennai? When someone is advised to use an oxygen concentrator at home—whether due to chronic respiratory conditions, post-COVID recovery, or other medical
Oxygen Concentrator vs Cylinder — Which Is Safer? When it comes to oxygen therapy, one of the most common questions patients and caregivers ask is: “Which is safer — an
Oxygen Concentrator Maintenance Checklist A oxygen concentrator If you or a loved one relies on an , you know how vital it is to ensure it functions properly every day.
Reliable Oxygen Concentrator for Clinic In modern medical care, a reliable oxygen concentrator is one of the most essential pieces of equipment for any clinic or healthcare facility. Whether it’s
DeVilbiss Oxygen Concentrator Dealer When it comes to oxygen therapy and respiratory care, choosing the right equipment and dealer makes all the difference. Among the leading names in the global
High Flow Oxygen Concentrator for Cardiac Patients For individuals with heart conditions, maintaining proper oxygen levels is crucial. A high flow oxygen concentrator provides a steady and controlled supply of
Oxygen Concentrator for Post Cardiac Intervention Recovering from a cardiac intervention—such as angioplasty, bypass surgery, or stent placement—requires special care and monitoring. One key factor that supports faster and safer