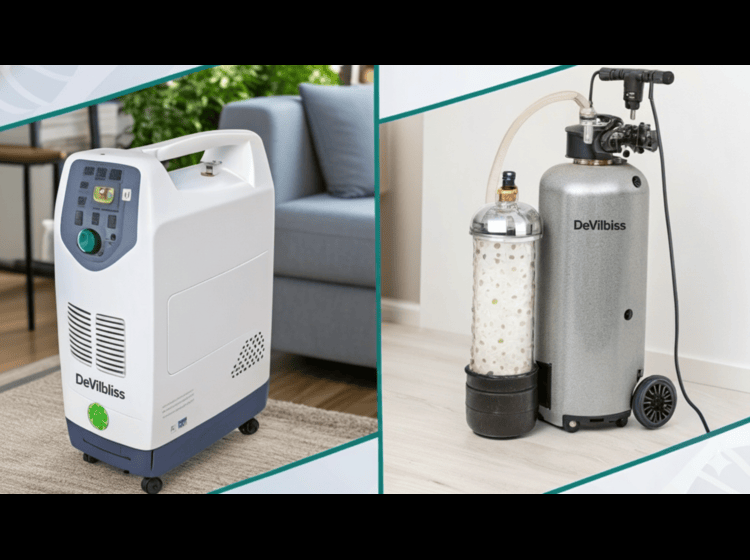
Oxygen Concentrator vs Cylinder – Which Is Better for Home Use?
Both devices serve the same purpose — delivering oxygen — but they operate differently and suit different lifestyles. In this post, we’ll compare oxygen concentrators and oxygen cylinders in terms of efficiency, safety, cost, maintenance, and convenience to help you decide which one is better for home use.
Oxygen Concentrator vs Cylinder Analysis
1. Understanding the Basics
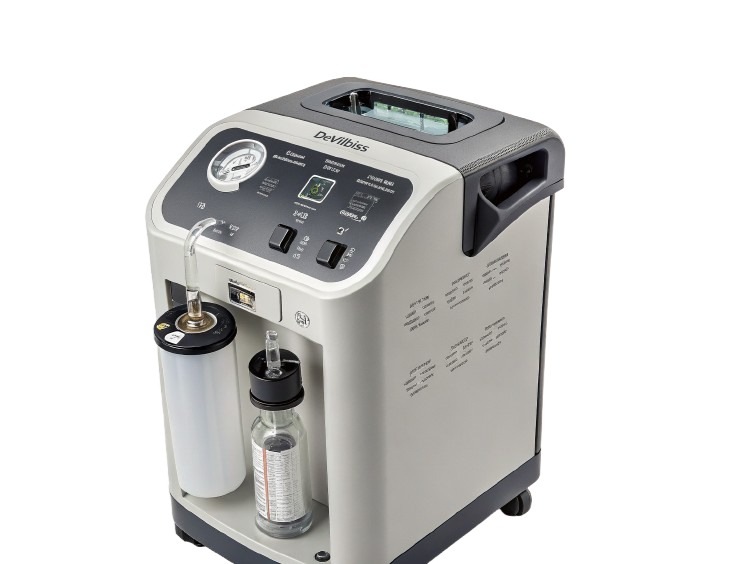
Oxygen Concentrator:An oxygen concentrator is an electronic medical device that draws air from the surroundings, filters out nitrogen, and delivers purified oxygen to the patient. It provides a continuous and steady supply of oxygen as long as it’s plugged into a power source.There are two main types:
- Home (stationary) concentrators – ideal for continuous use indoors.
- Portable concentrators – lightweight, battery-powered, and travel-friendly.
2. Oxygen Supply and Reliability
Concentrator:A major advantage of concentrators is that they generate oxygen continuously as long as there is electricity. There’s no need for refilling or replacing tanks. This makes them ideal for long-term home use.
However, concentrators rely entirely on electric power. During a power cut, the oxygen flow will stop unless you have a battery backup or generator.
Cylinder:
Cylinders are independent of electricity, making them more reliable during power outages or emergencies. But once the stored oxygen runs out, you must arrange a refill — which can be inconvenient or even risky if you run out unexpectedly.
✅ Best for reliability: Use a concentrator as the primary source and keep a cylinder as backup during power failures.
3. Safety Comparison
Safety is one of the biggest factors when deciding between the two.Oxygen Concentrator:
Concentrators produce oxygen on demand and do not store compressed gas. This greatly reduces the risk of fire or explosion.
Oxygen Cylinder:
Cylinders store oxygen under high pressure (up to 2000 psi). Mishandling, leakage, or exposure to flames can lead to accidents or fire hazards.
For home use, concentrators are generally safer, provided you keep them away from open flames, oil-based products, and smoking areas.
✅ Safety winner: Oxygen Concentrator
4. Ease of Use and Maintenance
Oxygen Concentrator:Operating a concentrator is simple — plug it in, set the flow rate, and start inhaling. Maintenance involves cleaning filters weekly and occasional professional servicing.
Oxygen Cylinder:
Cylinders require more effort — monitoring pressure, replacing regulators, and scheduling refills. Transporting heavy cylinders or handling high-pressure valves can be challenging for elderly patients.
✅ Easiest to use: Oxygen Concentrator
5. Oxygen Purity and Flow Rate
- Concentrators typically provide 90–96% oxygen purity, suitable for most home users.
- Cylinders provide 100% pure oxygen, but purity can drop if cylinders aren’t properly filled or maintained.
✅ Best for high-flow therapy: Oxygen Cylinder
✅ Best for continuous low-to-moderate flow: Oxygen Concentrator
6. Portability and Space
Oxygen Concentrator:Portable concentrators are compact and travel-friendly, but battery life is limited (usually 3–6 hours). Home models are heavier but have wheels for easy movement inside the house.
Oxygen Cylinder:
Cylinders, especially large ones, are bulky and heavy. Small portable cylinders exist but hold limited oxygen, requiring frequent refills.
✅ Portability winner: Portable Concentrator
7. Availability and Support
During high-demand periods (such as the COVID-19 pandemic), both cylinders and concentrators faced shortages. However, rental services and medical equipment providers in Chennai now offer both options with doorstep delivery and setup.When choosing, ensure the supplier provides:- 24/7 technical support
- Proper training for use
- Clean, well-maintained equipment
- Documentation and compliance certificates
8. Environmental and Practical Factors
Concentrators are eco-friendly, as they don’t require refills or transportation of heavy tanks. They simply use air and electricity. Cylinders require repeated filling and transport, which increases environmental impact and logistical hassle.✅ Eco-friendly choice: Oxygen Concentrator
Conclusion
Oxygen Concentrator Sale DeVilbiss brand is well-known for its durable, high-quality oxygen concentrators.These machines with features like quiet performance, steady oxygen flow, and easy maintenance, they’re an excellent choice for
Step-by-step guide - How to use an oxygen concentrator safely at home” oxygen concentrator have become essential medical devices for people with respiratory conditions such as COPD, asthma, pneumonia, and
Oxygen Concentrator vs Cylinder – Which Is Better for Home Use? When it comes to home oxygen therapy, choosing the right device is crucial for your health, comfort, and safety.
How Much Does Oxygen Concentrator Rental Cost in Chennai? When someone is advised to use an oxygen concentrator at home—whether due to chronic respiratory conditions, post-COVID recovery, or other medical
Oxygen Concentrator vs Cylinder — Which Is Safer? When it comes to oxygen therapy, one of the most common questions patients and caregivers ask is: “Which is safer — an
Oxygen Concentrator Maintenance Checklist A oxygen concentrator If you or a loved one relies on an , you know how vital it is to ensure it functions properly every day.
Reliable Oxygen Concentrator for Clinic In modern medical care, a reliable oxygen concentrator is one of the most essential pieces of equipment for any clinic or healthcare facility. Whether it’s
DeVilbiss Oxygen Concentrator Dealer When it comes to oxygen therapy and respiratory care, choosing the right equipment and dealer makes all the difference. Among the leading names in the global
High Flow Oxygen Concentrator for Cardiac Patients For individuals with heart conditions, maintaining proper oxygen levels is crucial. A high flow oxygen concentrator provides a steady and controlled supply of
Oxygen Concentrator for Post Cardiac Intervention Recovering from a cardiac intervention—such as angioplasty, bypass surgery, or stent placement—requires special care and monitoring. One key factor that supports faster and safer